Blockchain Toolkit for Dubai Future Foundaton
Dubai Future Foundation approached us wanting to create a website introducing and explaining the usage of Blockchain in various contexts. This effort aligns with the strategy of the Dubai Future Foundation: imagining, designing, and executing Dubai’s future.

About the client
Our client, The Dubai Future Foundation, builds a cohesive innovation ecosystem that includes accelerator programs, incubators, labs, regulatory sandboxes, and knowledge platforms – all to challenge the status quo and design a future-ready city powered by strong leadership and trailblazing disruptors. We teamed up and developed our Blockchain Toolkit website to support them in achieving their goals.
Dubai Future Foundation is ambitious and bold in its inspiring goals. Their enthusiasm and openness helped us envision, design, and deliver our solution for them.
About the project
The project aims to guide its users through developing and deploying a new blockchain solution. In addition, it can show you tools, resources, and know-how for undertaking blockchain projects.
Blockchain is popular, but communities and organizations need more understanding of its suitability and effectiveness. As such, the public comprehensiveness of blockchain technology challenges its solution-oriented goal. Therefore, we created a website representation of the Toolkit, along with tools, checklists, and practical guides, to ensure that blockchain implementation is meaningful and efficient.
UX and visual design representation
The entire Toolkit is available in the Arabic language. For us, as a Europe-based company, this presented an interesting undertaking. How do we approach specific cultural and design expectations? For example, how do we manage the right-to-left Arabic script and order of the user interface elements?
The Arabic script has specific styles, and word length might differ from English versions. Additionally, the translation of infographics and their adjustments was a challenge. But with the Foundation’s support and some internal know-how, we successfully tackled this challenge.
After tackling this challenge and finding the right piece of text to be placed in the infographic, another obstacle became obvious and needed some attention.
Right-to-left text direction
The strings we copied and pasted were left to right — LTR — but instead, they needed to be right to left — RTL.
Luckily, we use Figma as our design platform. Figma can be extended with useful plugins, and one of them solved our problems of flipping text to achieve RTL orientation (RTL PLZ Handoff). Although this workaround turned out to be useful for design purposes, it was complex to prepare it for implementation on the live pages as the text was flipped with the plugin.
The only solution was to manually copy and paste from the text file — a challenging procedure that required considerable time investment.
From the design point of view, the accessibility features of this project were pretty straightforward. In addition, the interface was designed to have high contrast, which served very well since it also solved the challenges that typically arise in these situations and accessibility (low contrasts).
Technical solution
The implementation covered all the requirements, including a user-friendly interface for easy administration and maintenance based on a WordPress platform.
We relied on our custom-built and designed blocks (so-called ‘Gutenberg blocks’) throughout the process. Carefully imagined and structured, they enabled us to be efficient and rapidly build pages while, at the same time, maintaining quality. Additionally, this approach enabled our client to achieve creative and organizational freedom for possible future updates: no vendor lock-in and no need to spend time and resources on most content-related tasks.
Content management system
We also added support for the CMS admin interface in the local language to better perform those content-related tasks and have a good user experience for editors. As a result, content creation, updates, and content representation on the public-facing Toolkit can be consistent and coherent experiences.
Another interesting feature we developed was an extension of the Blocks (Gutenberg) editor to support footnotes. That feature is not available out of the box and requires us to envision how we can best support this expectation. Editors can add footnotes and references all over the content, and our solution will collect and systematically organize them according to the order editors insert them into the content.
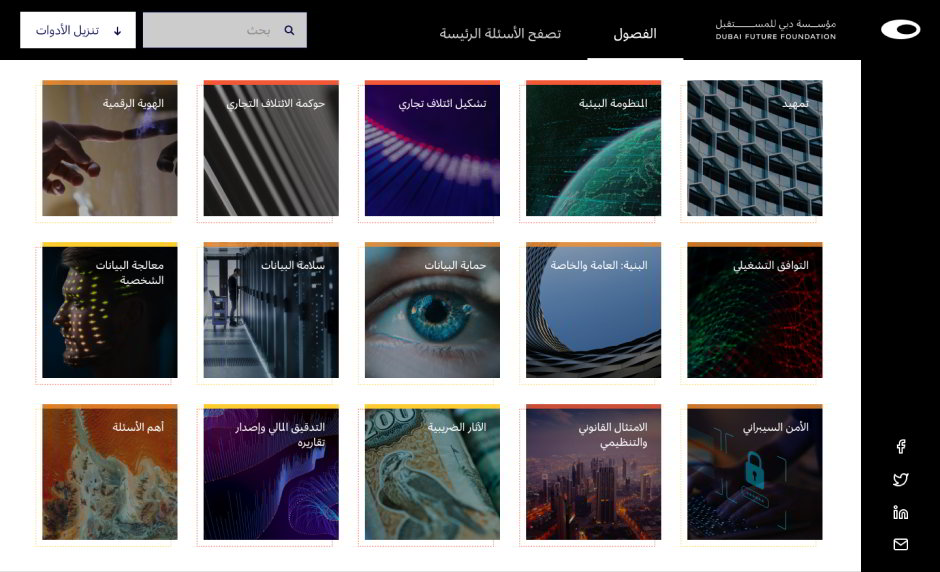
User testing and quality assurance
We conducted user testing by applying our standardized internal testing protocols and procedures. Our know-how and heuristics based on our experiences were valuable in these efforts. All our testing endeavors became even more critical when dealing with the tests related to the text orientation of the Arabic script and the order of items.
To assist the Foundation’s team in easily working on their new solution, we prepared easy-to-use documentation and held a remote training session.
Let’s work together!
We are excited to see how many businesses and organizations will use this Blockchain Toolkit and ensure better, more reliable, valuable, and meaningful implementations of blockchain technology.
Let us know if you’d like to learn more about this project or reach out to us to discuss your next project with us.